HR and Employment Law Basics
-
What is human resources (HR)?
Summary of the Employment Relations Act 2000
Are there different types of employment agreements?
What goes in an individual employment agreement?
Where do I start with the employment process?
Where should I start with workplace policies?
What is human resources(HR)?
Human Resources is the term used to describe an organisations responsibilities and activities related to managing and developing people. The following diagram shows what some of the key responsibilities are for you as an employer.
Summary of the Employment Relations Act 2000
The Employment Relations Act 2000 (ERA) sets out the terms and conditions of employment agreements, which sets minimum employment standards and protects the rights of employees. The following are additional laws that detail your legal obligations as an employer.
Holidays Act 2003 - Guidance on annual holidays, family violence leave, bereavement leave, alternative holidays, public holidays and sick leave.
Fair Pay Agreements Act 2022 - Provides a framework for collective bargaining for fair pay agreements (FPAs) across an entire occupation or industry.
Minimum Wage Act 1983 - Provides for a minimum wage, which is reviewed annually by the government. Basis for the 40-hour working week.
Human Rights Act 1993 - Containing laws against discrimination on a range of protected characteristics
Health and Safety at Work Act 2015 - Protection of workers and PCBU from workplace health and safety risks, so far as is reasonably practicable. This includes risks to both physical and mental health.
Are there different types of employment agreements?
In New Zealand, there are two main types of employment agreements:
Individual Employment Agreement (IEA)
Between an employer and an individual employee.
Individual negotiation.
Individual agreement sets out the terms and conditions
Collective Employment Agreement (CEA)
Between an employer and a registered union representing a group of employees.
Collective negotiation through the union.
Collective agreement sets out the terms and conditions.
What goes in a individual employment agreement?
An Individual Employment Agreement (IEA) in New Zealand must contain certain key elements to ensure compliance with employment laws and provide clarity on the terms and conditions of employment.
Termination
Confidentiality
Intellectual Property
Health and Safety
Dispute Resolution
Variation of Agreement
Signatures and Date
Names of the Parties
Position and Duties
Hours of Work
Contract Term
Remuneration
Leave Entitlements
Probationary Period
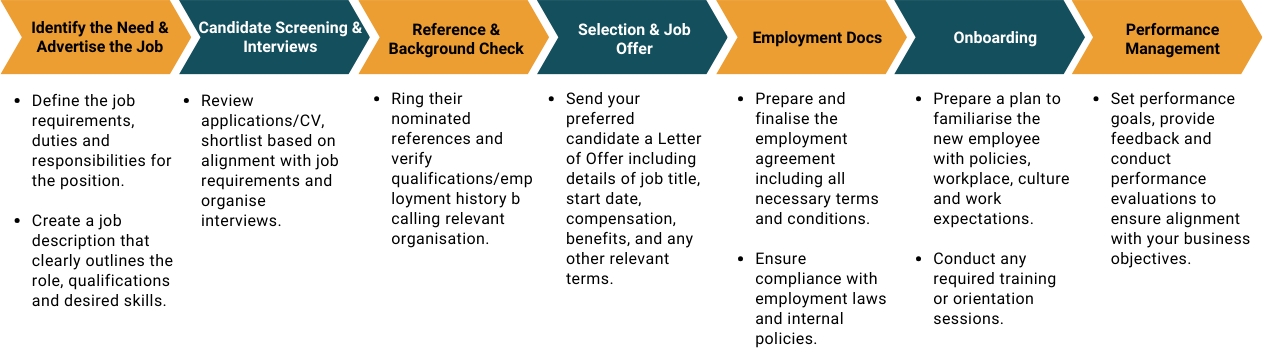
Where do I start with the employment process?
Below is an example of the typical stages you might go through when looking for and hiring new kaimahi.
In the construction industry, the employment process may involve additional steps to address the specific requirements and considerations of the industry.
Where should I start with workplace policies?
Several workplace policies and procedures can help establish clear guidelines, promote safety, and ensure smooth operations. While policies set the overarching principles and expectations, procedures provide specific guidelines on how to comply with those policies in various situations.
Quick Breakdown of Terminology:
Procedures explain the way something should be done (Applying for Annual Leave)
Code can be used as another way of describing a policy (Code of Conduct)
Guidelines provide a framework for things to consider when making a decision (Stakeholder Engagement)
Policy: Healthy and Safety
Procedures: Incident Reporting, Hazard Identification, Emergency Response, PPP, Worksite Safety and Safe Work Practices, Health & Hygiene.
Policy: Drug and Alcohol Policy
Procedures: Drug and Alcohol Testing, Reporting and Disciplinary Process.
Policy: Code of Conduct
Procedures: Complaint Handling, Conflict of Interest.
Policy: Environmental
Procedures: Environmental Incident Reporting, Waste Management, Sediment and Erosion Control, Environmental Impact Assessment.
Policy: Quality Assurance
Procedures: Material Inspection and Testing, Construction Documentation Control, Quality Control Inspections, Non-Conformance Management.
Policy: Travel
Procedures: Travel Booking Procedure, Reimbursement Guidelines, Travel Safety Measures, Approval Process.